Recombinant Antibodies
Experience exceptional batch-to-batch consistency, reproducible experimental results, and guaranteed long-term supply with SouthernBiotech's recombinant antibodies.
Shop Popular Recombinant Antibodies
Choose SouthernBiotech for Recombinant Antibodies that Help You Succeed
You have many choices when it comes to buying recombinant monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Here's why SouthernBiotech should be your primary choice:
- Quality proven over four decades of success. Scientists have been buying antibodies from us since the company was founded in 1982, long before many of our competitors even existed.
- Results you can trust ensured through in-house validation. Whatever product or service you purchase from us, you get results that allow you to move forward with confidence because all products are tested with our own hands in our own facility.
- Superior customer support. We sincerely care about your success and work with you to ensure our products work the way you need them to.
Factors to consider when choosing traditional vs. recombinant antibodies
Polyclonal secondary antibodies are popular for scientific research because they can provide signal amplification. This is due to their ability to bind multiple epitopes on each primary antibody, which increases the likelihood of detecting scarce antigens. In addition, since polyclonal secondary antibodies have been used for decades, they are seen as trusted reagents for many different immunoassay techniques.
We offer an extensive selection of polyclonal secondary antibodies that are cross-adsorbed against multiple species, including products for detecting mouse, rat, rabbit, goat, human, and chicken IgG.
Recombinant monoclonal secondary antibodies are produced by sequencing an existing antibody clone and synthesizing it in an expression host. Mammalian expression hosts such as Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) or human embryonic kidney (HEK) cells are preferred over bacterial or insect systems since they can replicate the post-translational modifications and protein folding required for antibodies to function effectively.
Alternatively, recombinant monoclonal secondary antibodies can be produced via phage display. This involves immobilizing the target of interest on a solid surface and incubating it with a phage library, comprising large numbers of phages that each express a different antibody single-chain variable fragment (scFv). Once binding has taken place, the phages are eluted and screened to identify the highest affinity binders, then the antibody encoding DNA is expressed in a mammalian cell line.
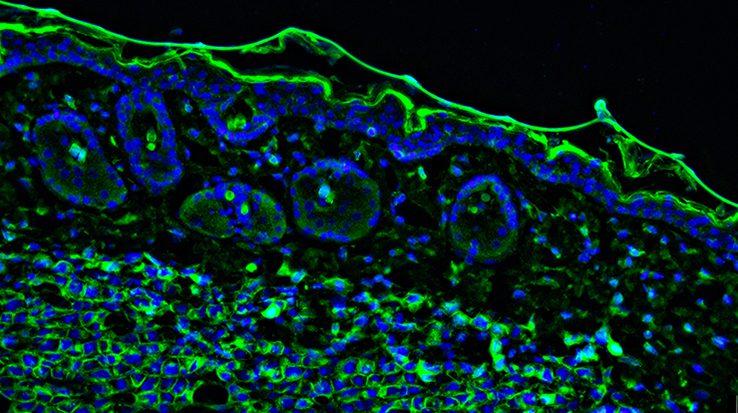
Recombinant monoclonal secondary antibodies offer several important advantages for scientific research. First, because the antibody DNA sequence is known, batch-to-batch consistency is guaranteed, assuring experimental reproducibility for a broad range of immunoassay applications. Knowing the DNA sequence also provides opportunities for engineering, such as to optimize antibody performance within a particular experimental setting.
Another major advantage of recombinant monoclonal secondary antibodies is that they reduce, or even eliminate, the need for animal use since they are produced using in vitro methods. In turn, this overcomes the issue of inter-animal variation, which can be especially challenging for researchers when an existing host animal is no longer available and experimental protocols must be re-optimized, as well as resulting in significantly faster production times.
Further benefits of recombinant monoclonal secondary antibodies include their scalability, which assures continuous supply and makes them useful for long-term studies, and the level of precision and accuracy they afford. For example, by selecting for highly specific antibodies during the recombinant cloning process, it is possible to avoid unwanted cross-reactivities that might give rise to false positive results later on.
Our recombinant mAbs include anti-human IgG, IgA1, and lambda, anti-rabbit IgG, and we are actively expanding our product range.