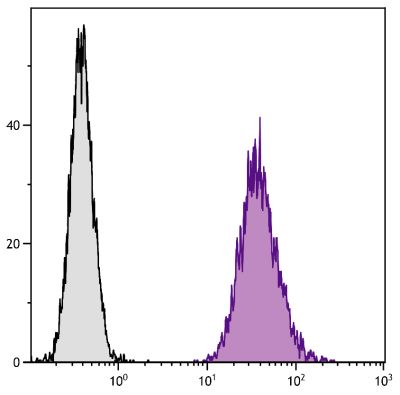
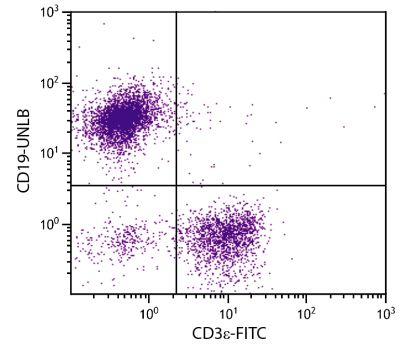
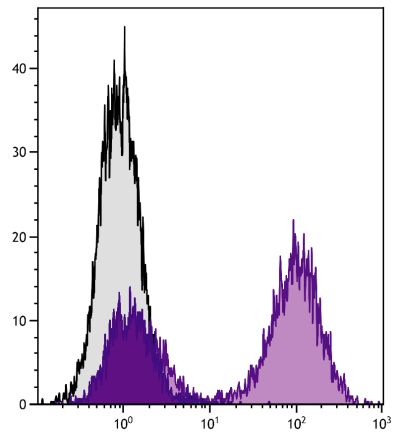
Rat Anti-Mouse CD40-UNLB (1C10)
Cat. No.:
1645-01
Purified Anti-Mouse CD40 antibody for use in flow cytometry, immunoprecipitation, activation, and blocking assays.
$228.00
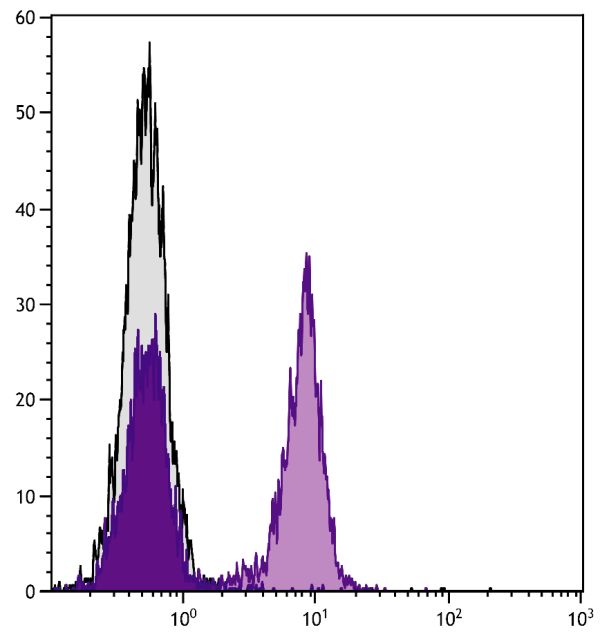
| Clone | 1C10 |
|---|---|
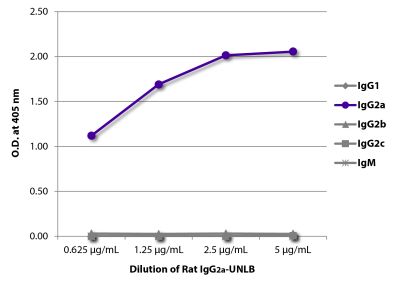
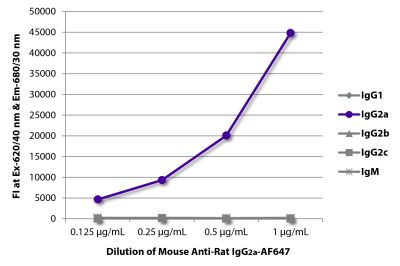
| Isotype | Rat (Lewis) IgG2aκ |
| Isotype Control | Rat IgG2a-UNLB (KLH/G2a-1-1) |
| Specificity | Mouse CD40 |
| Alternative Names | TNFRSF5, Bp50 |
| Description | CD40 is a type I cell surface protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor superfamily of cell surface receptors. In mice it is expressed on B lineage cells, follicular dendritic cells, thymic epithelium, and interdigitating cells in the T-cell zone of secondary lymphoid organs. CD40 first becomes detectable on a subset of small pre-B II cells in bone marrow with the levels of CD40 expression increasing thereafter during B cell maturation. Immature B cells (IgM+IgDloB220lo) express intermediate levels of CD40, whereas mature B cells (IgM+IgDhiB220hi) express high levels. CD40 has a central role in B cell growth and differentiation, and signaling through CD40 in combination with IL-4 reportedly induces immunoglobulin isotype switching and secretion of IgE. The agonistic 1C10 antibody closely resembles gp39/CD40 ligand in its ability to stimulate proliferation of small, resting B lymphocytes in the absence of other cofactors. |
| Immunogen | sCD40 |
| Conjugate | UNLB (Unconjugated) |
| Buffer Formulation | Borate buffered saline, pH 8.2 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C |
| Applications |
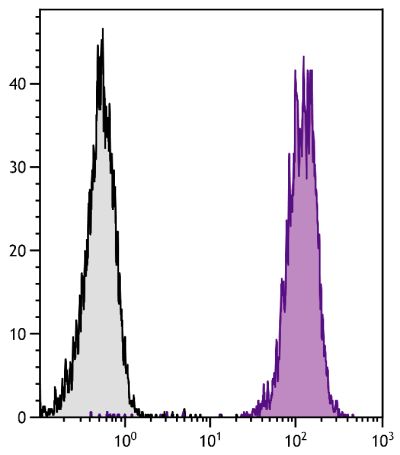
Flow Cytometry – Quality tested 1,7-12 Immunoprecipitation – Reported in literature 1 Activation – Reported in literature 1-4 Blocking – Reported in literature 5,6 |
| RRID Number | AB_2795083 |
| Gene ID |
21939 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Symbol |
Cd40 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Aliases | IGM; p50; Bp50; GP39; IMD3; TRAP; HIGM1; T-BAM; Tnfrsf5; AI326936 |
| UniProt ID |
P27512 (Mouse |
| UniProt Name |
TNR5_MOUSE (Mouse) |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Heath AW, Wu WW, Howard MC. Monoclonal antibodies to murine CD40 define two distinct functional epitopes. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24:1828-34. (Immunogen, FC, IP, Activ)
- 2. Randall TD, Heath AW, Santos-Argumedo L, Howard MC, Weissman IL, Lund FE. Arrest of B lymphocyte terminal differentiation by CD40 signaling: mechanism for lack of antibody-secreting cells in germinal centers. Immunity. 1998;8:733-42. (Activ)
- 3. Nojima T, Hayashi K, Goitsuka R, Nakayama K, Nakayama K, Kitamura D. Double knockout mice show BASH and PKCδ have different epistatic relationships in B cell maturation and CD40-mediated activation. Immunol Lett. 2006;105:48-54. (Activ)
- 4. Rolph MS, Kaufmann SH. CD40 signaling converts a minimally immunogenic antigen into a potent vaccine against the intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 2001;166:5115-21. (Activ)
- 5. Kluiver JL, Chen CZ. MicroRNAs regulate B-cell receptor signaling-induced apoptosis. Genes Immun. 2012;13:239-44. (Block)
- 6. Baker RL, Wagner DH Jr, Haskins K. CD40 on NOD CD4 T cells contributes to their activation and pathogenicity. J Autoimmun. 2008;31:385-92. (Block)
- 7. Brannan CA, Roberts MR. Resident microglia from adult mice are refractory to nitric oxide-inducing stimuli due to impaired NOS2 gene expression. Glia. 2004;48:120-31. (FC)
- 8. Zaru R, Mollahan P, Watts C. 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 deficiency perturbs toll-like receptor signaling events and actin cytoskeleton dynamics in dendritic cells. J Biol Chem. 2007;283:929-39. (FC)
- 9. Brix S, Lund P, Kjaer TM, Straarup EM, Hellgren LI, Frøkiær H. CD4+ T-cell activation is differentially modulated by bacteria-primed dendritic cells, but is generally down-regulated by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Immunology. 2010;129:338-50. (FC)
- 10. Teixeira L, Botelho AS, Mesquita SD, Correia A, Cerca F, Costa R, et al. Plasmacytoid and conventional dendritic cells are early producers of IL-12 in Neospora caninum-infected mice. Immunol Cell Biol. 2010;88:79-86. (FC)
- 11. Chen Y, Adams E, Regateiro FS, Vaux DJ, Betz AG, Andersen KG, et al. Activation rather than Foxp3 expression determines that TGF-β-induced regulatory T cells out-compete naïve T cells in dendritic cell clustering. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42:1436-48. (FC)
- 12. Jacobsen J, Haabeth OW, Tveita AA, Schjetne KW, Munthe LA, Bogen B. Naive idiotope-specific B and T cells collaborate efficiently in the absence of dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2014;192:4174-83. (FC)
See All References