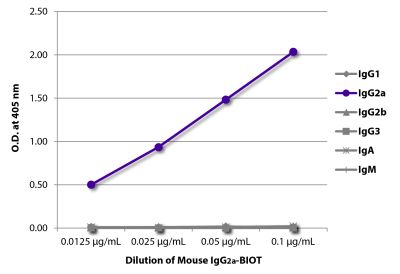
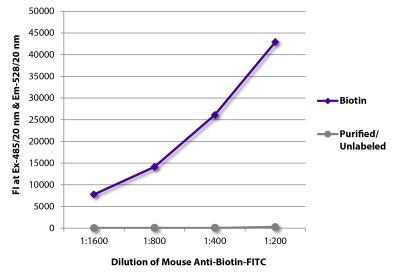
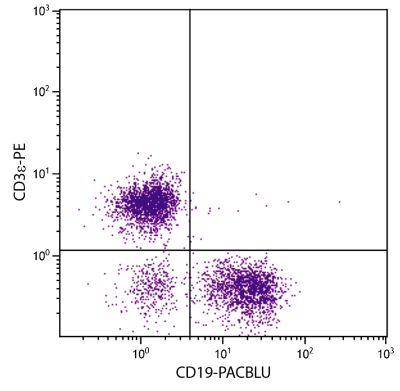
Mouse Anti-Mouse H-2Kk-BIOT (36-7-5)
Cat. No.:
1917-08
Biotin Anti-Mouse H-2Kk antibody for use in flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry assays.
$261.00
| Clone | 36-7-5 |
|---|---|
| Isotype | Mouse (A.TL) IgG2aκ |
| Isotype Control | Mouse IgG2a-BIOT (HOPC-1) |
| Specificity | Mouse H-2Kk |
| Alternative Names | MHC Class I |
| Description | The monoclonal antibody 36-7-5 reacts with the H-2Kk MHC class I alloantigen. Cross-reactivity with splenocytes of SJL/Hsd mice has been observed by flow cytometry. The antibody does not react with other (e.g., b, d, q) haplotypes. |
| Immunogen | A.AL mouse splenocytes |
| Conjugate | BIOT (Biotin) |
| Buffer Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline containing < 0.1% sodium azide |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C |
| Applications |
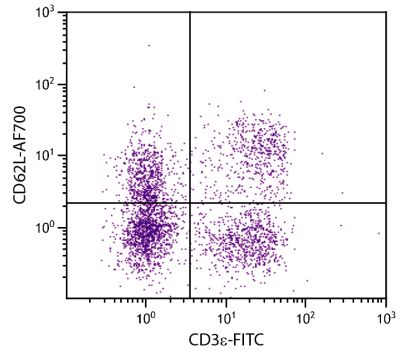
Flow Cytometry – Quality tested 3 Immunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections – Reported in literature 2 |
| RRID Number | AB_2795528 |
| Gene ID |
14972 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Symbol |
H2-K1 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Aliases | H-2K; H-2K(d); H2-D1; H2-K; K-f |
| UniProt ID |
P04223 (Mouse |
| UniProt Name |
HA1K_MOUSE (Mouse) |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Sachs DH, Mayer N, Ozato K.Hybridoma antibodies directed toward murine H-2 and Ia antigens. In: Hämmerling GJ, Hämmerling U, Kearney JF, editors. Monoclonal antibodies and T-cell hybridomas. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1981. p.95-101 (Immunogen)
- 2. Ardehali A, Laks H, Drinkwater DC, Ziv E, Drake TA, . Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 is induced on vascular endothelia and medial smooth muscle cells in experimental cardiac allograft vasculopathy. Circulation. 1995;92:450-6. (IHC-FS)
- 3. Sykes M, Harty MW, Karlhofer FM, Pearson DA, Szot G, Yokoyama W. Hematopoietic cells and radioresistant host elements influence natural killer cell differentiation. J Exp Med. 1993;178:223-9. (FC)