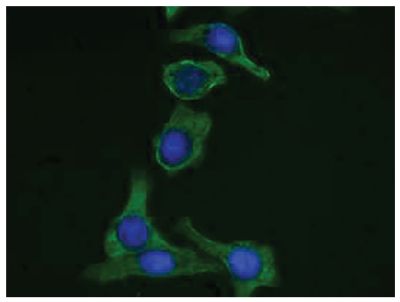
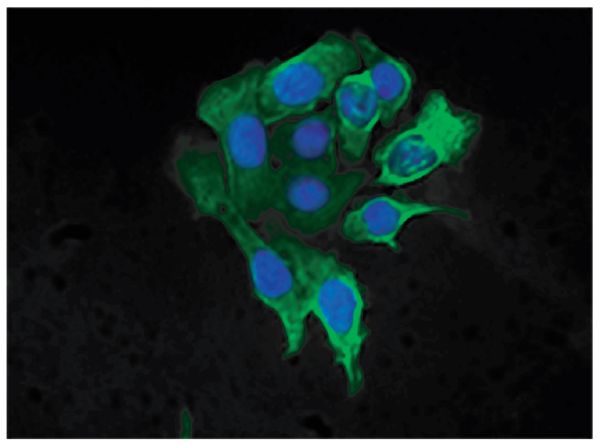
Mouse Anti-Cytokeratin 8-FITC (SB37b)
Cat. No.:
10080-02
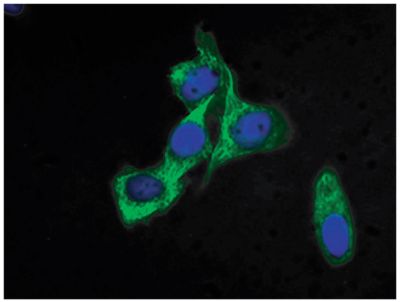
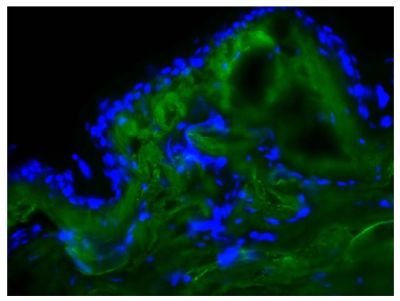
FITC Anti-Cytokeratin 8 antibody for use in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry / immunocytochemistry, and western blot assays.
$278.00
| Clone | SB37b |
|---|---|
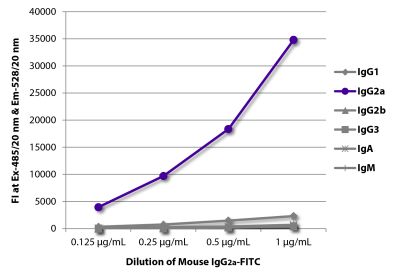
| Isotype | Mouse (BALB/c) IgG2aκ |
| Isotype Control | Mouse IgG2a-FITC (HOPC-1) |
| Specificity | Cytokeratin 8 |
| Alternative Names | CK 8, keratin 8 |
| Description | Keratins are a family of intermediate filament proteins that assemble into filaments through forming heterodimers of one type I keratin (keratins 9 to 23) and one type II keratin (keratins 1-8). The two keratin types share only 30% sequence homology. Keratins demonstrate tissue- and differentiation-specific expression profiles. Cytokeratin 8 belongs to the type B (basic) subfamily of keratins and exists in combination with keratin 18. It is expressed in all simple type epithelia tissues (e.g., liver, pancreas, kidney, gut epithelial lining) but not in stratified squamous epithelia. Cytokeratin 8 is also present in the majority of adenocarcinomas and ductal carcinomas but is absent in most squamous cell carcinomas. |
| Immunogen | Recombinant C-terminal cytokeratin 8 |
| Conjugate | FITC (Fluorescein) |
| Buffer Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline containing < 0.1% sodium azide |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Volume | 0.2 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C; Avoid exposure to light |
| Applications |
Immunocytochemistry – Quality tested 1 ELISA – Quality tested Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin Sections – Reported in literature 2 Flow Cytometry 3 Western Blot 3 Immunoprecipitation 3 |
| RRID Number | AB_2794111 |
| Gene ID |
3856 (Human) 16691 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Symbol |
KRT8 (Human) Krt8 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Aliases | CARD2; CK-8; CK8; CYK8; K2C8; K8; KO K8; Card2; EndoA; Krt2-8; Krt-2.8; AA960620; AL022697; AU019895 |
| UniProt ID |
P05787 (Human P11679 (Mouse |
| UniProt Name |
K2C8_HUMAN (Human) K2C8_MOUSE (Mouse) |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Chatin B, Mével M, Devallière J, Dallet L, Haudebourg T, Peuziat P, et al. Liposome-based formulation for intracellular delivery of functional proteins. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2015;4:e244. (ICC)
- 2. Wang D. Individualized cardiovascular medicine: identifying new mechanisms to inhibit the development of myointimal hyperplasia [dissertation]. Hamburg (Germany): University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf; 2015. (IHC-PS)
- 3. SouthernBiotech unpublished data (FC, WB, IP)