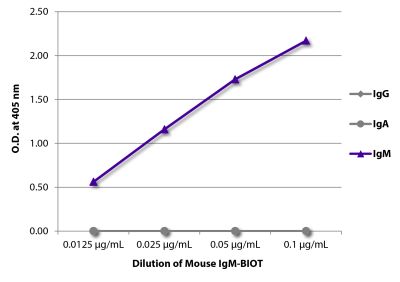
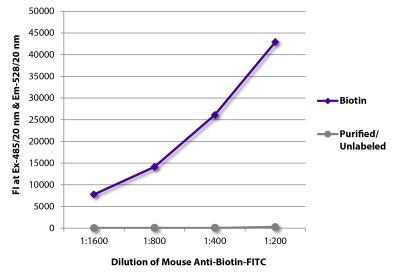
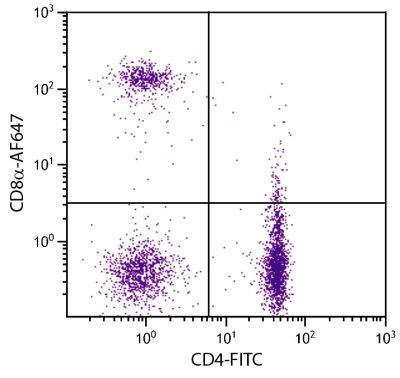
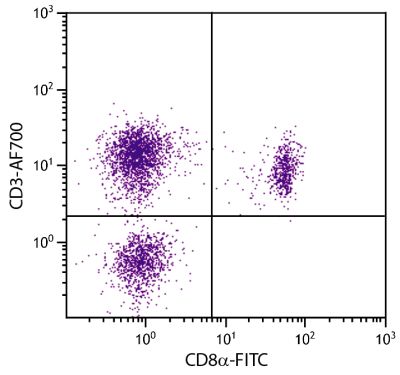
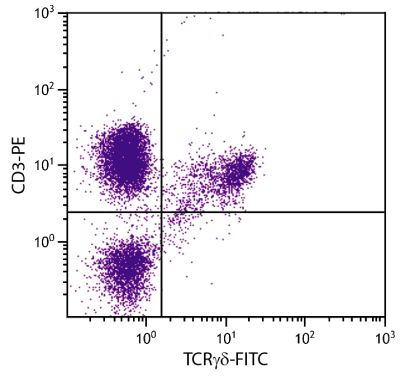
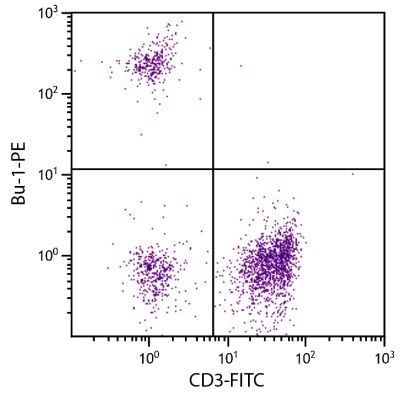
Mouse Anti-Chicken Ia-BIOT (CIa)
Cat. No.:
8290-08
Biotin Anti-Chicken Ia antibody for use in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry / immunocytochemistry, and immunoprecipitation assays.
$353.00

| Clone | CIa |
|---|---|
| Isotype | Mouse (BALB/c) IgMκ |
| Isotype Control | Mouse IgM-BIOT (11E10) |
| Specificity | Chicken/Quail/Dove/Pigeon/Duck Ia |
| Alternative Names | MHC Class II |
| Description | The chicken Ia antigen is expressed on B cells, a subpopulation of the monocyte/macrophage lineage of cells, and mitogen-activated T cells. The molecule recognized by this antibody is similar in structure to the murine Ia antigens and human DR antigens. |
| Immunogen | Splenic leukocytes from an outbred nine-week-old chicken |
| Conjugate | BIOT (Biotin) |
| Buffer Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline containing < 0.1% sodium azide |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C |
| Applications |
Flow Cytometry – Quality tested 1,7,9,10 Immunohistochemistry-Frozen Sections – Reported in literature 2-6 Immunocytochemistry – Reported in literature 1,7,8 Immunoprecipitation – Reported in literature 1 Blocking – Reported in literature 1 |
| RRID Number | AB_2796484 |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Ewert DL, Munchus MS, Chen CH, Cooper MD. Analysis of structural properties and cellular distribution of avian Ia antigen by using monoclonal antibody to monomorphic determinants. J Immunol. 1984;132:2524-30. (Immunogen, FC, ICC, IP, Block, Quail, Dove, Pigeon, & Duck Reactivity)
- 2. Wang X, Efr GF. Apoptosis in feathers of Smyth line chickens with autoimmune vitiligo. J Autoimmun. 2004;22:21-30. (IHC-FS)
- 3. O'Halloran EK, Oesterle EC. Characterization of leukocyte subtypes in chicken inner ear sensory epithelia. J Comp Neurol. 2004;475:340-60. (IHC-FS)
- 4. Das SC, Nagasaka N, Yoshimura Y. Changes in the localization of antigen presenting cells and T cells in the utero-vaginal junction after repeated artificial insemination in laying hens. J Reprod Dev. 2005;51:683-7. (IHC-FS)
- 5. Subedi K, Yoshimura Y. Expression of MHC class I and II in growing ovarian follicles of young and old laying hens, Gallus domesticus. J Poult Sci. 2005;42:101-9. (IHC-FS)
- 6. Yoshimura Y, Fukui T, Nishibori M, Isobe N. Effects of age and gonadal steroids on the localization of antigen presenting cells in the epididymis of the male chicken, Gallus domesticus. J Reprod Dev. 2006;52:363-71. (IHC-FS)
- 7. Bakri Y, Sarrazin S, Mayer UP, Tillmanns S, Nerlov C, Boned A, et al. Balance of MafB and PU.1 specifies alternative macrophage or dendritic cell fate. Blood. 2005;105:2707-16. (FC, ICC)
- 8. Niikura M, Kim T, Hunt HD, Burnside J, Morgan RW, Dodgson JB, et al. Marek's disease virus up-regulates major histocompatibility complex class II cell surface expression in infected cells. Virology. 2007;359:212-9. (ICC)
- 9. Rautenschlein S, Subramanian A, Sharma JM. Bioactivities of a tumour necrosis-like factor released by chicken macrophages. Dev Comp Immunol. 1999;23:629-40. (FC)
- 10. Chrząstek K, Piasecki T, Wieliczko A. Impact of CpG oligodeoxynucleotide stimulation on percentage of T and B cells in chicken. Pol J Vet Sci. 2013;16:551-4. (FC)
See All References