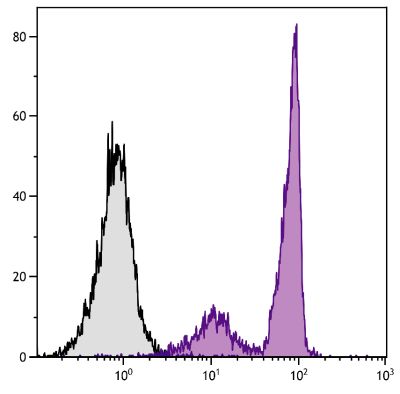
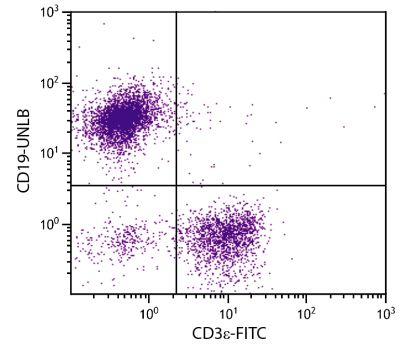
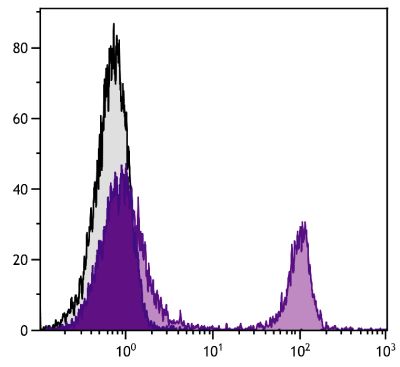
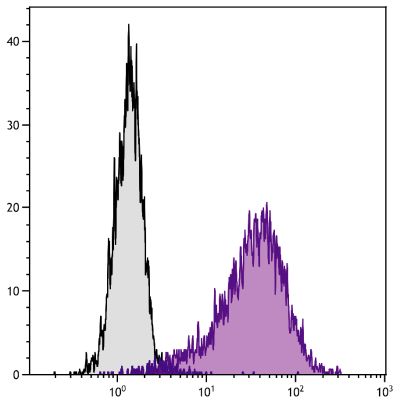
Hamster Anti-Mouse CD28-UNLB (PV-1)
Cat. No.:
1615-01
Purified Anti-Mouse CD28 antibody for use in flow cytometry, immunoprecipitation, costimulation, and stimulation assays.
$223.00
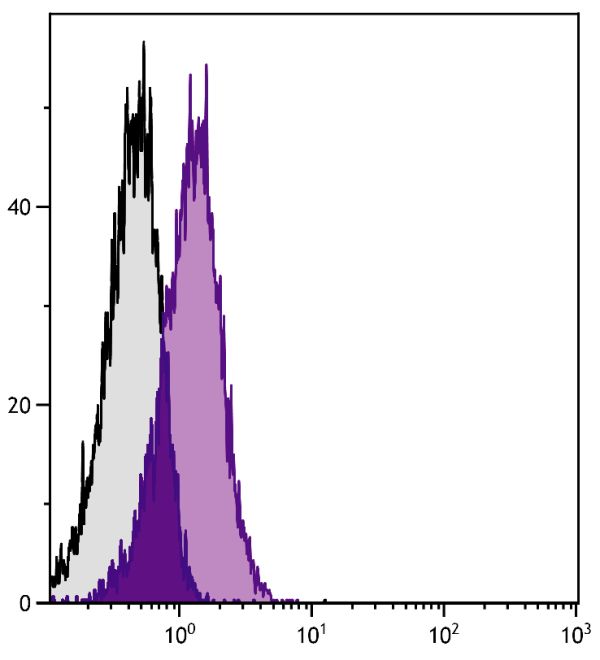
| Clone | PV-1 |
|---|---|
| Isotype | Hamster (Armenian) IgG2 |
| Isotype Control | Hamster IgG-UNLB |
| Specificity | Mouse CD28 |
| Alternative Names | Tp44, T44 |
| Description | CD28 is a type I disulfide-linked homodimer that is constitutively expressed on most thymocytes, at low density on nearly all CD4+ and CD8+ peripheral T lymphocytes and at very low levels on NK cells. Its expression is upregulated upon T-cell activation. CD28 is a ligand for CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2) on B cells and other antigen presenting cells and plays an important role in the interaction between T cells and B cells. CD28 is a costimulatory receptor involved in many, but not all, T-cell independent immune responses. |
| Immunogen | C57BL/6N mouse T cell lymphoma EL4 cell line |
| Conjugate | UNLB (Unconjugated) |
| Buffer Formulation | Borate buffered saline, pH 8.2 |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C |
| Applications |
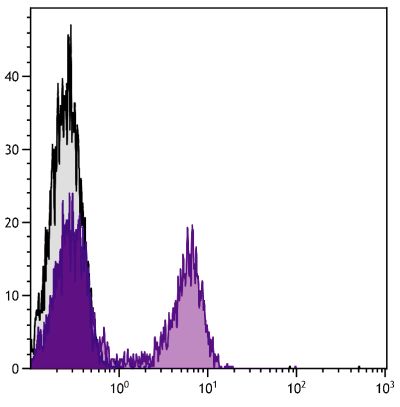
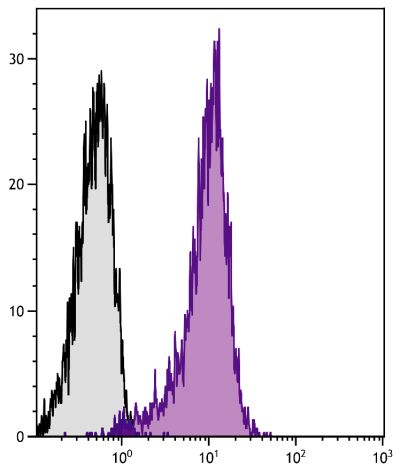
Flow Cytometry – Quality tested 1,6 Immunoprecipitation – Reported in literature 1,2 Costimulation – Reported in literature 1,3,4 Stimulation – Reported in literature 5 |
| RRID Number | AB_2795029 |
| Gene ID |
12487 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Symbol |
Cd28 (Mouse) |
| UniProt ID |
P31041 (Mouse |
| UniProt Name |
CD28_MOUSE (Mouse) |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Abe R, Vandenberghe P, Craighead N, Smoot DS, Lee KP, June CH. Distinct signal transduction in mouse CD4+ and CD8+ splenic T cells after CD28 receptor ligation. J Immuno. 1995;154:985-97. (Immunogen, FC, IP, Costim)
- 2. Dodson LF, Boomer JS, Deppong CM, Shah DD, Sim J, Bricker TL, et al. Targeted knock-in mice expressing mutations of CD28 reveal an essential pathway for costimulation. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:3710-21. (IP)
- 3. Kanzaki M, Wada J, Sugiyama K, Nakatsuka A, Teshigawara S, Murakami K, et al. Galectin-9 and T cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 pathway is a therapeutic target for type 1 diabetes. Endocrinology. 2012;153:612-20. (Costim)
- 4. Tomimori Y, Tanaka Y, Goto M, Fukuda Y. Repeated topical challenge with chemical antigen elicits sustained dermatitis in NC/Nga mice in specific-pathogen-free condition. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:119-24. (Costim)
- 5. Zhang T, Fresnay S, Welty E, Sangrampurkar N, Rybak E, Zhou H, et al. Selective CD28 blockade attenuates acute and chronic rejection of murine cardiac allografts in a CTLA-4-dependent manner. Am J Transplant. 2011;11:1599-1609. (Stim)
- 6. Jacobsen J, Haabeth OW, Tveita AA, Schjetne KW, Munthe LA, Bogen B. Naive idiotope-specific B and T cells collaborate efficiently in the absence of dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2014;192:4174-83. (FC)
See All References