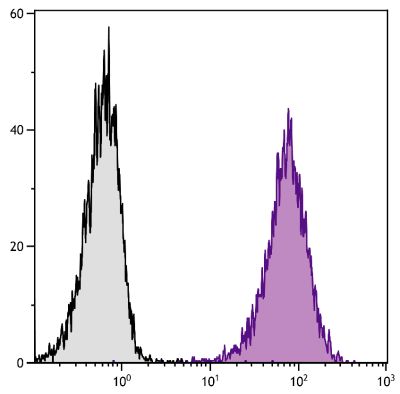
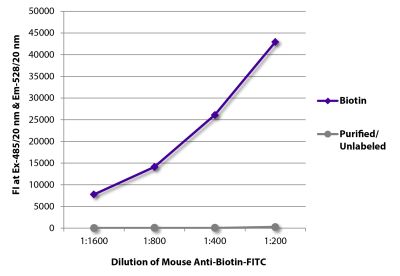
Hamster Anti-Mouse CD28-BIOT (37.51)
Cat. No.:
1610-08
Biotin Anti-Mouse CD28 antibody for use in flow cytometry and immunoprecipitation assays.
$261.00

| Clone | 37.51 |
|---|---|
| Isotype | Hamster (Syrian) IgG2 |
| Isotype Control | Hamster IgG-BIOT |
| Specificity | Mouse CD28 |
| Alternative Names | Tp44, T44 |
| Description | CD28 is a type I disulfide-linked homodimer that is constitutively expressed on most thymocytes, at low density on nearly all CD4+ and CD8+ peripheral T lymphocytes and at very low levels on NK cells. Its expression is upregulated upon T-cell activation. CD28 is a ligand for CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2) on B cells and other antigen presenting cells and plays an important role in the interaction between T cells and B cells. CD28 is a costimulatory receptor involved in many, but not all, T-cell independent immune responses. |
| Immunogen | C57BL/6N mouse T cell lymphoma EL-4 cell line |
| Conjugate | BIOT (Biotin) |
| Buffer Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline containing < 0.1% sodium azide |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C |
| Applications |
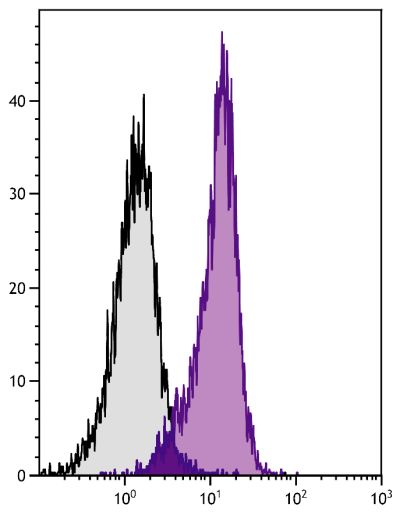
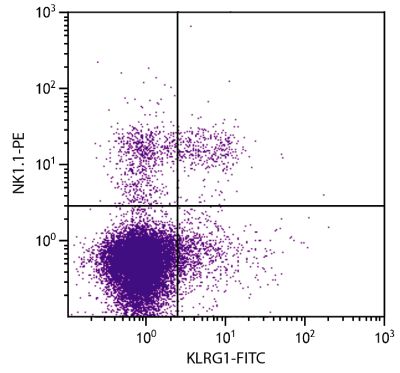
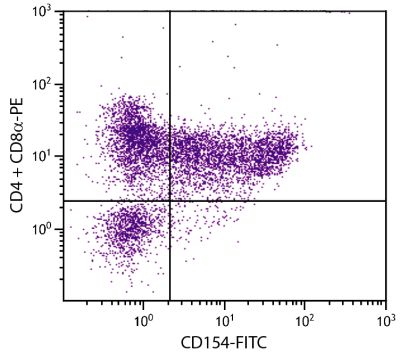
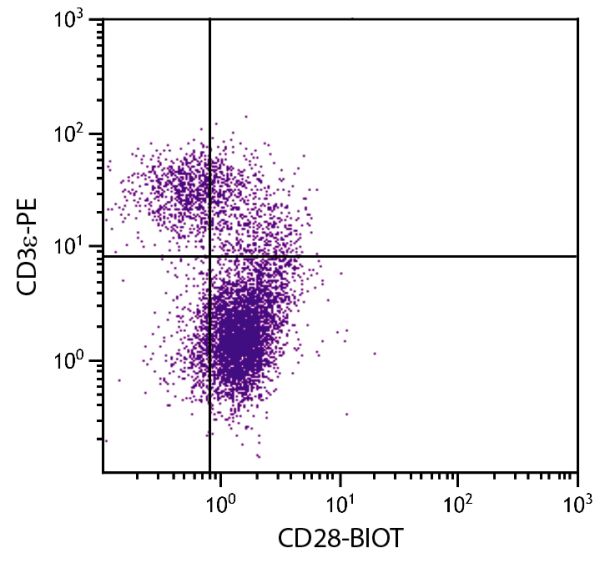
Flow Cytometry – Quality tested 1,2 Immunoprecipitation – Reported in literature 1 Costimulation – Reported in literature 1-3,7-9,11 Stimulation – Reported in literature 10 Activation – Reported in literature 5 Blocking – Reported in literature 6 |
| RRID Number | AB_2795023 |
| Gene ID |
12487 (Mouse) |
| Gene ID Symbol |
Cd28 (Mouse) |
| UniProt ID |
P31041 (Mouse) |
| UniProt Name |
CD28_MOUSE (Mouse) |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Gross JA, Callas E, Allison JP. Identification and distribution of the costimulatory receptor CD28 in mouse. J Immunol. 1992;149:380-8. (Immunogen, FC, IP, Costim)
- 2. Silverio JC, Pereira IR, Cipitelli M, Vinagre NF, Rodrigues MM, Gazzinelli RT, et al. CD8+ T-cells expressing interferon gamma or perforin play antagonistic roles in heart injury in experimental Trypanosoma cruzi-elicited cardiomyopathy. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(4):e1002645. (Costim)
- 3. Lin J, Harding A, Giurisato E, Shaw AS. KSR1 modulates the sensitivity of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway activation in T cells without altering fundamental system outputs. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:2082-91. (Costim)
- 4. Nandi D, Gross JA, Allison JP. CD28-mediated costimulation is necessary for optimal proliferation of murine NK cells. J immunol. 1994;152:3361-9. (FC, Costim)
- 5. Cibotti R, Punt JA, Dash KS, Sharrow SO, Singer A. Surface molecules that drive T cell development in vitro in the absence of thymic epithelium and in the absence of lineage-specific signals. Immunity. 1997;6:245-55. (Activ)
- 6. Nishio M, Spielman J, Lee RK, Nelson DL, Podack ER. CD80 (B7.1) and CD54 (intracellular adhesion molecule-1) induce target cell susceptibility to promiscuous cytotoxic T cell lysis. J Immunol. 1996;157:4347-53. (Block)
- 7. Kim EH, Sullivan JA, Plisch EH, Tejera MM, Jatzek A, Choi KY, et al. Signal integration by Akt regulates CD8 T cell effector and memory differentiation. J Immunol. 2012;188:4305-14. (Costim)
- 8. Yoshida K, Sakamoto A, Yamashita K, Arguni E, Horigome S, Arima M, et al. Bcl6 controls granzyme B expression in effector CD8+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2006;36:3146-56. (Costim)
- 9. Belhacéne N, Gamas P, Gonçalvès D, Jacquin M, Beneteau M, Jacquel A, et al. Severe thymic atrophy in a mouse model of skin inflammation accounts for impaired TNFR1 signaling. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47321. (Costim)
- 10. Zhang T, Fresnay S, Welty E, Sangrampurkar N, Rybak E, Zhou H, et al. Selective CD28 blockade attenuates acute and chronic rejection of murine cardiac allografts in a CTLA-4-dependent manner. Am J Transplant. 2011;11:1599-1609. (Stim)
- 11. Shen XZ, Okwan-Doudu D, Blackwell W, Ong FS, Janjulia T, Bernstein EA. Myeloid expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme facilitates myeloid maturation and inhibits the development of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Lab Invest. 2014;94:536-44. (Costim)
See More