Goat Anti-Bovine IgG(H+L)-FITC
Cat. No.:
6030-02
Goat Anti-Bovine IgG(H+L)-FITC antibody for use in flow cytometry, immunocytochemistry, and western blot assays.
$58.00
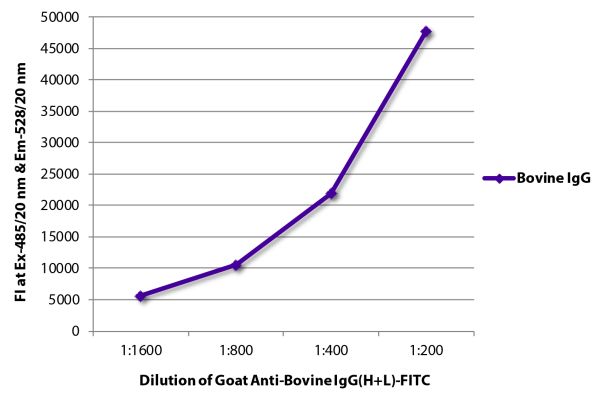

| Isotype | Goat IgG |
|---|---|
| Isotype Control | Goat IgG-FITC |
| Specificity | Reacts with the heavy and light chains of bovine IgG |
| Source | Pooled antisera from goats hyperimmunized with bovine IgG |
| Cross Adsorption | None; may react with immunoglobulins from other species and the light chains of other bovine immunoglobulins |
| Purification Method | Affinity chromatography on bovine IgG covalently linked to agarose |
| Conjugate | FITC (Fluorescein) |
| Buffer Formulation | Phosphate buffered saline containing < 0.1% sodium azide |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/mL |
| Volume | 1.0 mL |
| Recommended Storage | 2-8°C; Avoid exposure to light |
| Applications |
Quality tested applications for relevant formats include - ELISA 1-6 FLISA Other referenced applications for relevant formats include - Flow Cytometry 7 Immunocytochemistry 6,8 Immunoprecipitation 9 Western Blot 2,10 Purification 1 Surface Plasmon Resonance 11 |
| RRID Number | AB_2796110 |
Documentation
Certificate of Analysis Lookup
Enter the Catalog Number and Lot Number for the Certificate of Analysis you wish to view
- 1. Riedel M, Müller B, Wintermantel E. Protein adsorption and monocyte activation on germanium nanopyramids. Biomaterials. 2001;22:2307-16. (ELISA, Purification)
- 2. Liu J, Yu J, Wang M, Liu Q, Zhang W, Deng C, et al. Serodiagnosis of Neospora caninum infection in cattle using a recombinant tNcSRS2 protein-based ELISA. Vet Parasitol. 2007;143:358-63. (ELISA, WB)
- 3. Juleff N, Windsor M, Lefevre EA, Gubbins S, Hamblin P, Reid E, et al. Foot-and-mouth disease virus can induce a specific and rapid CD4+ T-cell-independent neutralizing and isotype class-switched antibody response in naïve cattle. J Virol. 2009;83:3626-36. (ELISA)
- 4. Cui J, Zhang B, Lin Y, Wang Q, Qian A, Nakane A, et al. Protective effect of glutathione S-transferase-fused mutant staphylococcal enterotoxin C against Staphylococcus aureus-induced bovine mastitis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2010;135:64-70. (ELISA)
- 5. Otto W, Najnigier B, Stelmasiak T, Robins-Browne RM. Randomized control trials using a tablet formulation of hyperimmune bovine colostrum to prevent diarrhea caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in volunteers. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46:862-8. (ELISA)
- 6. Mertens M, Vatansever Z, Mrenoshki S, Krstevski K, Stefanovska J, Djadjovski I, et al. Circulation of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus in the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia revealed by screening of cattle sera using a novel enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015;9(3):e0003519. (ELISA, ICC)
- 7. Guirnalda P, Murphy NB, Nolan D, Black SJ. Anti-Trypanosoma brucei activity in Cape buffalo serum during the cryptic phase of parasitemia is mediated by antibodies. Int J Pathol. 2007;37:1391-9. (FC)
- 8. Basso W, Lesser M, Grimm F, Hilbe M, Sydler T, Trösch L, et al. Bovine besnoitiosis in Switzerland: imported cases and local transmission. Vet Parasitol. 2013;198:265-73. (ICC)
- 9. Foucras G, Corbière F, Tasca C, Pichereaux C, Caubet C, Trumel C, et al. Alloantibodies against MHC class I: a novel mechanism of neonatal pancytopenia linked to vaccination. J Immunol. 2011;187:6564-70. (IP)
- 10. Odunuga OO, Shazhko A. Ammonium sulfate precipitation combined with liquid chromatography is sufficient for purification of bovine serum albumin that is suitable for most routine laboratory applications. Bio Chem Comp. 2013; 1:3 http://dx.doi.org/10.7243/2052-9341-1-3. (WB)
- 11. Indyk HE, Williams JW, Patel HA. Analysis of denaturation of bovine IgG by heat and high pressure using an optical biosensor. Int Dairy J. 2008;18:359-66. (Surface Plasmon Resonance)
See All References